

Buffer solutions have a definite pH.Bodies to function properly, the pH of our blood has to be
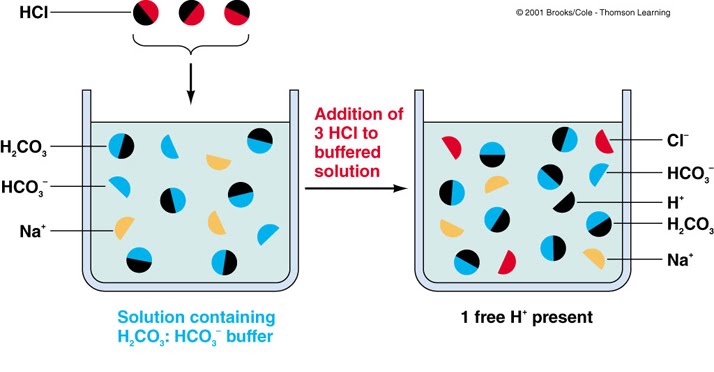
In this way, the OH – ions of NaOH are removed and the pH is almost unaltered.

Now, if you add a drop of NaOH, the OH – ions react with the free acid to give undissociated water molecules. Thus, there is a very slight change in the pH value. To this, if you add a drop of a strong acid like HCl, the H + ions from HCl combine with CH 3COO – to give feebly ionized CH 3COOH. Here, acetic acid is weakly ionized while sodium acetate is almost completely ionized. So, how does a buffer work? Let’s take the example of a mixture of acetic acid (CH 3COOH) and sodium acetate (CH 3COONa). Understand the Concept of Equilibrium in Chemical Process in detail here. Buffers can either be prepared by mixing a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its conjugate acid.įor example, phosphate buffer, a commonly used buffer in research labs, consists of a weak base (HPO 4 2-) and its conjugate acid (H 2PO 4 –). If you know the pK a (acid dissociation constant) of the acid and pK b (base dissociation constant) of the base, then you can make a buffer of known pH by controlling the ratio of salt and acid or salt and base. Buffer solutions help maintain the pH of many different things as shown in the image below. For example, a mixture of ammonium chloride and ammonium hydroxide acts as a buffer solution with a pH of about 9.25. For example, a mixture of acetic acid and sodium acetate acts as a buffer solution with a pH of about 4.75.Īlkaline buffers, on the other hand, have a pH above 7 and contain a weak base and one of its salts. Acidic buffers are solutions that have a pH below 7 and contain a weak acid and one of its salts. Types of Buffer Solutionsīuffers are broadly divided into two types – acidic and alkaline buffer solutions. Learn more about pH Scale here in more detail.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
